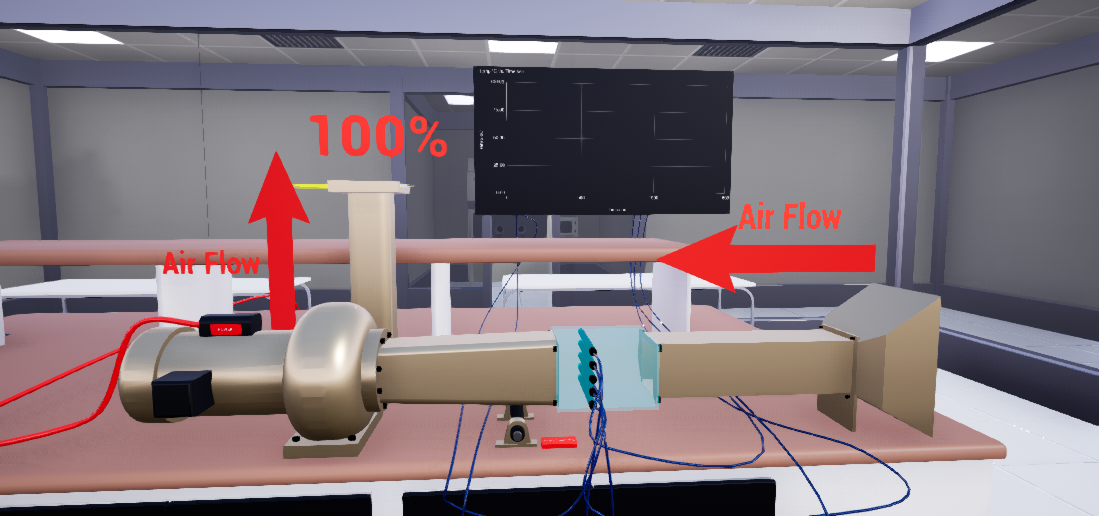
Revolutionizing Thermodynamics Education
With Virtual Reality
Thermodynamics, a branch of physics that deals with the relationships between heat, energy, and work, is a critical subject for students pursuing careers in engineering, chemistry, and other scientific disciplines. Traditional methods of teaching thermodynamics often involve hands-on laboratory work, which can be time-consuming, expensive, and logistically challenging. In recent years, virtual labs have emerged as an innovative and powerful educational tool, providing a more effective and efficient way to teach thermodynamics. In this article, we will explore the benefits of using virtual labs to teach thermodynamics, highlighting the advantages over traditional learning methods.
1. Unlimited Access to Laboratory Experiments:One of the most significant benefits of virtual labs is the ability to provide students with unlimited access to laboratory experiments. Traditional lab environments are typically limited by factors such as space, equipment availability, and time constraints. These limitations can hinder students' ability to fully explore and understand the concepts they are learning. In contrast, virtual labs allow students to conduct experiments anytime and anywhere, as long as they have access to a computer and an internet connection. This unlimited access not only helps students build a stronger foundation in thermodynamics but also encourages them to take ownership of their learning, as they can explore and experiment at their own pace.
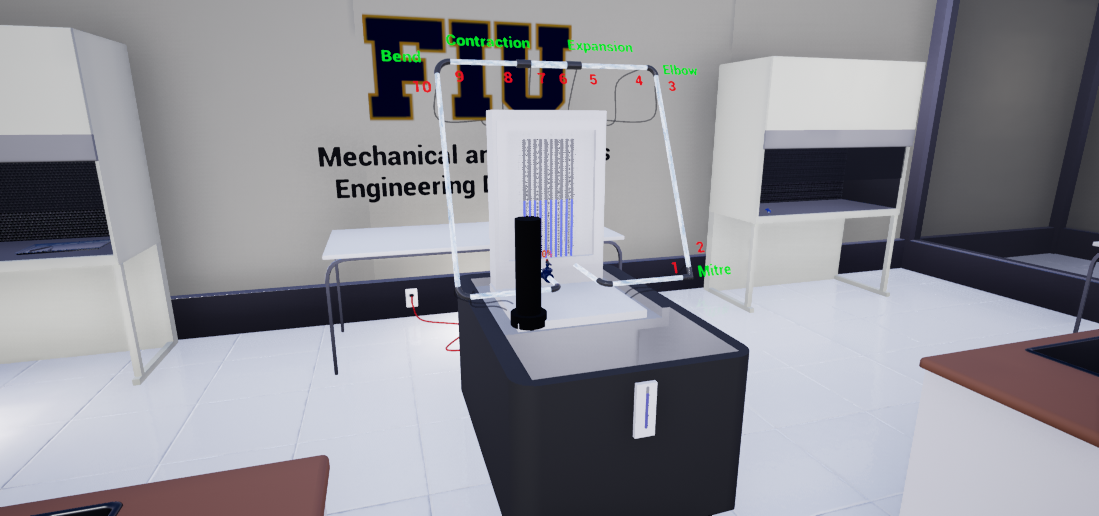
2. Enhanced Visualization and Understanding of Concepts:Thermodynamics involves complex concepts and mathematical equations that can be difficult for students to visualize and comprehend. Virtual labs provide an interactive and immersive learning experience, enabling students to manipulate variables and see the effects in real-time. This enhanced visualization helps students better understand the underlying principles of thermodynamics and fosters a deeper appreciation for the subject.
3. Cost-Effective:Setting up and maintaining a traditional laboratory for thermodynamics education can be expensive, requiring a significant investment in equipment, chemicals, and other consumables. Additionally, there is often a need for trained lab technicians and instructors to guide students through the experiments. Virtual labs, on the other hand, are a more cost-effective solution, as they eliminate the need for physical lab infrastructure and reduce the costs associated with equipment maintenance and consumables. Virtual labs can also be easily scaled up to accommodate a larger number of students, making them an attractive option for educational institutions looking to expand their thermodynamics curriculum without incurring significant additional costs.
4. Improved Safety and Environmental Sustainability:Working with chemicals, high-pressure systems, and heat sources in a traditional thermodynamics lab can pose safety risks for students and instructors. Virtual labs eliminate these risks, as students can conduct experiments in a controlled and safe virtual environment. This not only reduces the potential for accidents and injuries but also alleviates the anxiety some students may experience when working with potentially hazardous materials and equipment. Additionally, virtual labs contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing the consumption of chemicals and energy associated with traditional lab experiments. By minimizing waste and resource usage, virtual labs promote a more sustainable approach to thermodynamics education.
5. Flexible and Adaptable Learning Environment:Virtual labs offer a high degree of flexibility, allowing students to tailor their learning experience to their individual needs and preferences. Students can choose to focus on specific aspects of thermodynamics that they find particularly challenging or interesting, and they can easily revisit previous experiments to reinforce their understanding. This adaptability helps students become more engaged and motivated in their learning, leading to improved academic performance. Furthermore, virtual labs can be easily adapted to suit different learning styles and abilities. For example, students with visual impairments can use screen readers or other assistive technologies to access the virtual lab environment, while those with mobility impairments can participate in lab activities without the physical barriers that may be present in a traditional lab setting.
6. Encouraging Collaboration and Communication:Virtual labs can also facilitate collaboration and communication among students, as they can work together on experiments and share their results and insights with one another. This collaborative learning environment fosters a sense of community and teamwork, helping students develop critical interpersonal and communication skills that are essential for success in their future careers. In a traditional lab setting, students may work in small groups, limiting the exchange of ideas and perspectives. Virtual labs, however, enable students to connect with their peers from different geographical locations and cultural backgrounds, enriching the learning experience and promoting cross-cultural understanding.
7. Real-time Feedback and Assessment:One of the challenges in traditional thermodynamics lab education is providing timely and effective feedback to students. Instructors may not have the time or resources to closely monitor and assess each student's performance during lab sessions, which can lead to gaps in understanding or misconceptions. Virtual labs offer real-time feedback and assessment, enabling students to immediately identify and correct any errors or misunderstandings. This instant feedback helps students build a stronger foundation in thermodynamics, as they can learn from their mistakes and adjust their approach as needed. Additionally, this real-time assessment can help instructors identify areas where students may be struggling, allowing them to provide targeted support and guidance.
8. Seamless Integration with Online Learning Platforms:As online education continues to grow in popularity, virtual labs offer a seamless integration with various learning management systems (LMS) and other online learning platforms. This integration allows instructors to easily incorporate virtual lab activities into their existing curriculum, providing a comprehensive and cohesive learning experience for students. By combining the flexibility and convenience of online learning with the immersive and interactive nature of virtual labs, educators can create a highly effective and engaging learning environment that supports students' academic success in thermodynamics.
7. Real-time Feedback and Assessment:One of the challenges in traditional thermodynamics lab education is providing timely and effective feedback to students. Instructors may not have the time or resources to closely monitor and assess each student's performance during lab sessions, which can lead to gaps in understanding or misconceptions. Virtual labs offer real-time feedback and assessment, enabling students to immediately identify and correct any errors or misunderstandings. This instant feedback helps students build a stronger foundation in thermodynamics, as they can learn from their mistakes and adjust their approach as needed. Additionally, this real-time assessment can help instructors identify areas where students may be struggling, allowing them to provide targeted support and guidance.
The use of virtual labs to teach thermodynamics offers numerous advantages over traditional learning methods, including unlimited access to laboratory experiments, enhanced visualization and understanding of concepts, cost-effective and scalable solutions, improved safety and environmental sustainability, flexible and adaptable learning environments, collaboration and communication opportunities, real-time feedback and assessment, and seamless integration with online learning platforms.
By embracing these innovative educational tools, educators can revolutionize the way thermodynamics is taught and provide students with a more engaging, effective, and accessible learning experience. Ultimately, the adoption of virtual labs in thermodynamics education has the potential to better prepare students for success in their chosen fields, equipping them with a deep understanding of the subject and the essential skills needed for their future careers.
By Sofia Indira Calderón Alvarez
Contact Us